Check Snmp Version Windows

 -->
-->
This article describes how to configure the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Service in Windows Server 2003. This article describes how to configure SNMP agent properties, SNMP traps, and SNMP security.
- Install SNMP Agent and configure the community string. Orion Platform products use the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) to collect detailed information about your server. While configuring SNMP, certain values are already pre-configured for you. This is by-design, to ensure that your server is monitored properly.
- Click the Free Download button above to download the setup file for the current version of SNMP Tester. Execute the file Paessler SNMP Tester Setup.exe. Follow the steps in the Paessler SNMP Tester Setup Wizard. For more information on how to use SNMP Tester, see the SNMP Tester Manual.
- What command shows what SNMP Protocol version(s) 1, 2c, 3 I am running on my system? How do change the SNMP version in use? Answer: There is no command to show the current running SNMP version. The snmpd daemon will not show as running in any one particular version, as it has the ability to do any of the three at any time.
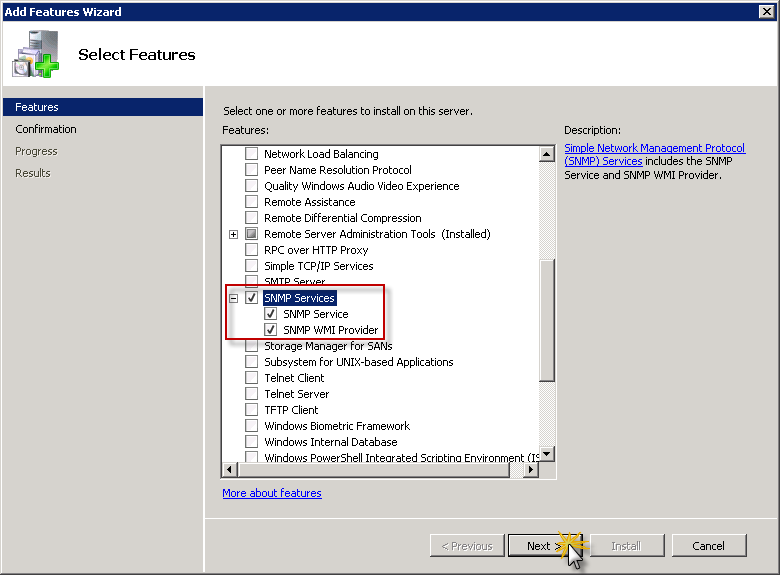
I can't find any official document about SNMP version supported on Windows Server 2008 R2 and later. As far as I know, Windows Server 2008 R2 only support SNMP v1 and SNMP v2c. If we want to upgrade the SNMP service to v3, we need to install some third-party SNMP services. Besides, SNMP has been deprecated on Windows Server 2012. This process is very similar on all Windows systems. Enabling SNMP on Windows 8 and 10 as well as Windows Server 12, 16, and 19. Open the Control Panel on your Windows machine. Click Turn Windows features on or off in section Programs. Click to enlarge. Check Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) and install it.
Applies to: Windows Server 2003
Original KB number: 324263
Summary
The SNMP Service, when configured for an agent, generates trap messages that are sent to a trap destination, if any specific events occur. For example, you can configure the SNMP service to send a trap when it receives a request for information that does not contain the correct community name and does not match an accepted host name for the service.
Configure SNMP agent information
Check Snmp Version Windows Server
Click Start, point to Control Panel, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Computer Management.
In the console tree, expand Services and Applications, and then click Services.
In the right pane, double-click SNMP Service.
Click the Agent tab.
Type the name of the user or administrator of the computer in the Contact box, and then type the physical location of the computer or contact in the Location box.
These comments are treated as text and are optional.
Under Service, click to select the check boxes next to the services that are provided by your computer. Service options are:
- Physical: Specifies whether the computer manages physical devices, such as a hard disk partition.
- Applications: Specifies whether the computer uses any programs that send data by using TCP/IP.
- Datalink and subnetwork: Specifies whether this computer manages a TCP/IP subnetwork or datalink, such as a bridge.
- Internet: Specifies whether this computer acts as an IP gateway (router).
- End-to-end: Specifies whether this computer acts as an IP host.
Click OK.
Snmp Check For Windows

Note
If you have installed additional TCP/IP network devices, such as a switch or a router, see Request for Comments (RFC) 1213 for additional information. To view RFC 1213, visit the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) Web site
Microsoft provides third-party contact information to help you find technical support. This contact information may change without notice. Microsoft does not guarantee the accuracy of this third-party contact information.
Configure SNMP communities and traps
Click Start, point to Control Panel, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Computer Management.
In the console tree, expand Services and Applications, and then click Services.
In the right pane, double-click SNMP Service.
Click the Traps tab.
In the Community name box, type the case-sensitive community name to which this computer will send trap messages, and then click Add to list.
Under Trap destinations, click Add.
In the Host name, IP or IPX address box, type the name, IP, or IPX address of the host, and then click Add.
The host name or address appears in the Trap destinations list.
Repeat steps 5 through 7 to add the communities and trap destinations that you want.
Click OK.
Check Snmp Version Windows 7
Configure SNMP security for a community
- Click Start, point to Control Panel, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Computer Management.
- In the console tree, expand Services and Applications, and then click Services.
- In the right pane, double-click SNMP Service.
- Click the Security tab.
- Click to select the Send authentication trap check box (if it is not already selected) if you want a trap message sent whenever authentication fails.
- Under Accepted community names, click Add.
- To specify how the host processes SNMP requests from the selected community, click the permission level that you want in the Community Rights box.
- In the Community Name box, type the case-sensitive community name that you want, and then click Add.
- Specify whether or not to accept SNMP packets from a host. To do so, do one of the following:
- To accept SNMP requests from any host on the network, regardless of identity, click Accept SNMP packets from any host.
- To limit the acceptance of SNMP packets, click Accept SNMP packets from these hosts, click Add, and then type the appropriate host name, IP, or IPX address in the Host name, IP or IPX address box.
- Click Add.
- Click OK.
Important
If you remove all of the community names, including the default name Public, SNMP does not respond to any community names that are presented.